Cancer Care
Cancer Care
Cancer refers to any one of a large number of diseases characterized by the development of abnormal cells that divide uncontrollably and have the ability to infiltrate and destroy normal body tissue. Cancer often has the ability to spread throughout your body.
Cancer is the second-leading cause of death in the world. But survival rates are improving for many types of cancer, thanks to improvements in cancer screening, treatment and prevention.

Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, which is also called gastric cancer, is a growth of cells that starts in the stomach. The stomach is in the upper middle part of the belly, just below the ribs. The stomach helps to break down and digest food.Stomach cancer can happen in any part of the stomach. In most of the world, stomach cancers happen in the main part of the stomach. This part is called the stomach body.
In the United States, stomach cancer is more likely to start by the gastroesophageal junction. This is the part where the long tube that carries food you swallow meets the stomach. The tube that carries food to the stomach is called the esophagus.Where the cancer starts in the stomach is one factor health care providers think about when making a treatment plan. Other factors might include the cancer’s stage and the type of cells involved. Treatment often includes surgery to remove the stomach cancer. Other treatments may be used before and after surgery.
Liver Cancer
Primary liver cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the liver. Cancer that forms in other parts of the body and spreads to the liver is not primary liver cancer. The liver is one of the largest organs in the body.Cancer that begins in the cells of the liver.
The liver is the football-sized organ in the upper-right area of the stomach.Symptoms are uncommon in the early stages of liver cancer. Later, symptoms may include weight loss, stomach pain, vomiting and yellowed skin.
Treatments vary but may include removal of part of the liver, transplant, chemotherapy and in some cases, radiation.


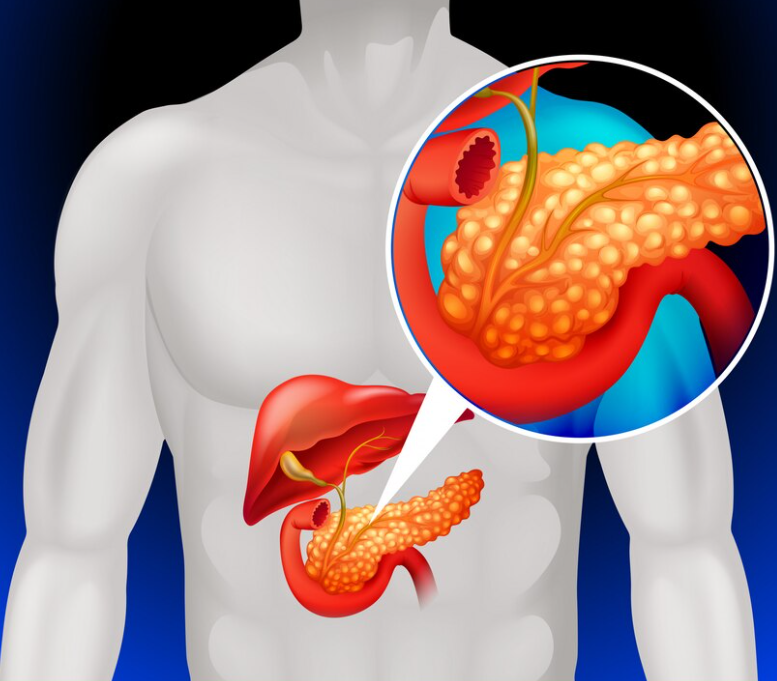
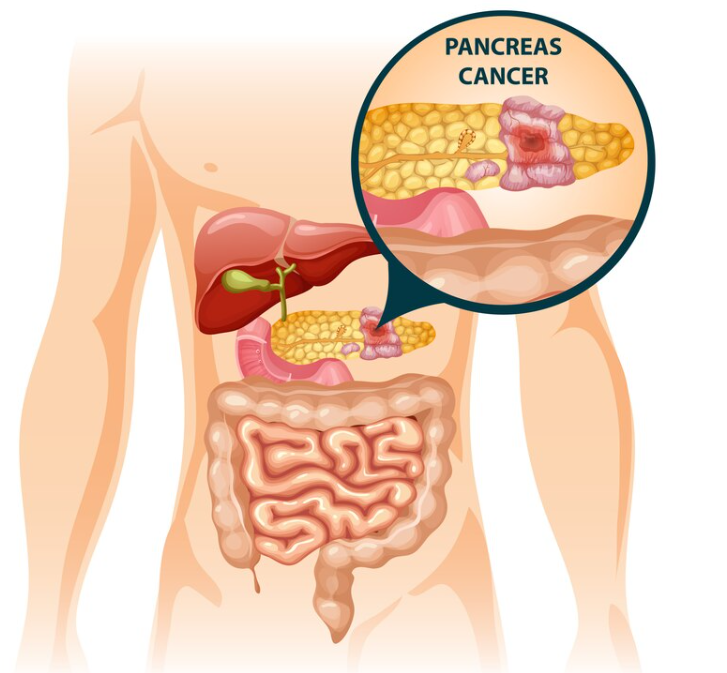
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer occurs when cells in your pancreas develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. These mutations tell the cells to grow uncontrollably and to continue living after normal cells would die. These accumulating cells can form a tumor.
Cancer that begins in the organ lying behind the lower part of the stomach (pancreas).The pancreas secretes enzymes that aid digestion and hormones that help regulate the metabolism of sugars. This type of cancer is often detected late, spreads rapidly and has a poor prognosis.
Bile Duct Cancer
Bile duct cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the bile ducts. Bile duct cancer is also called cholangiocarcinoma. A network of tubes, called ducts, connects the liver, gallbladder, and small intestine.
Adenocarcinomas, the most common type of extrahepatic bile duct cancer, form in the cells of the mucous gland lining the inside of the bile duct. Adenocarcinomas account for about 95 percent of all bile duct cancers. Bile duct adenocarcinoma is also called cholangiocarcinoma.
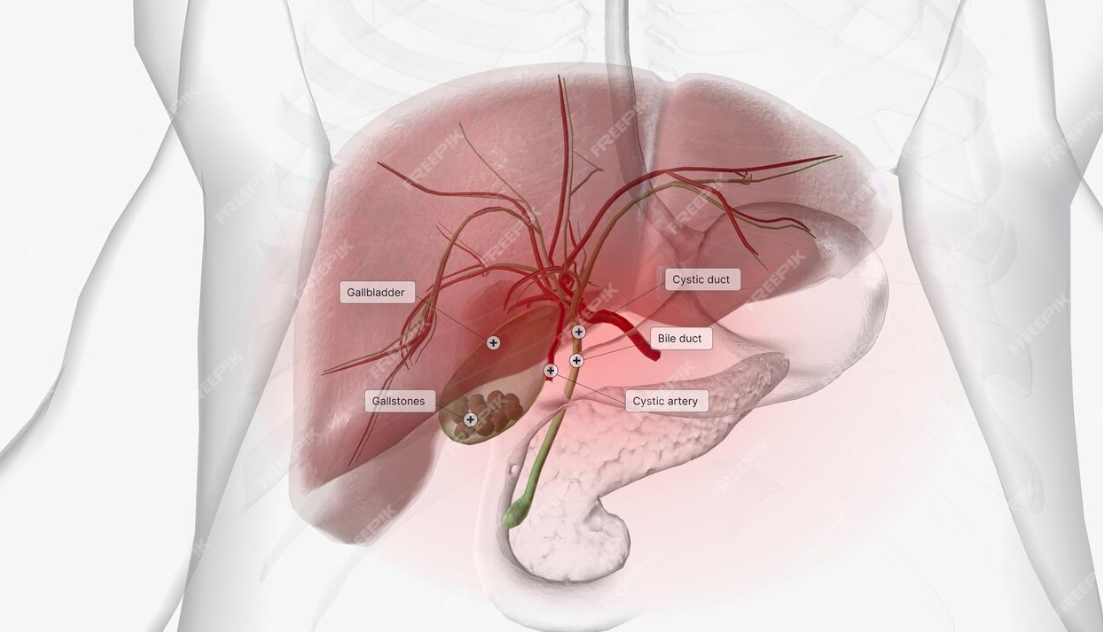
Gallstones Cancer
Gallstones are hard, pebble-like pieces of material, usually made of cholesterol or bilirubin, that form in your gallbladder. Gallstones can range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball. The gallbladder can make one large gallstone, hundreds of tiny stones, or both small and large stones.
A hardened deposit within the fluid in the gallbladder, a small organ under the liver.Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid.Gallstones can vary in size and number and may or may not cause symptoms.People who experience symptoms usually require gallbladder removal surgery. Gallstones that don’t cause symptoms usually don’t need treatment.
Pancreatic Cysts
Pancreatic cysts are saclike pockets of fluid on or in your pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces hormones and enzymes that help digest food. Pancreatic cysts are typically found during imaging testing for another problem.
Pancreatic cysts are fluid-filled growths that develop in the pancreas. This small glandular organ is located in the abdomen between the stomach and the intestines. In addition to making digestive enzymes, the endocrine (islet) cells in the pancreas produce hormones, such as insulin, that control blood sugar levels in your body.
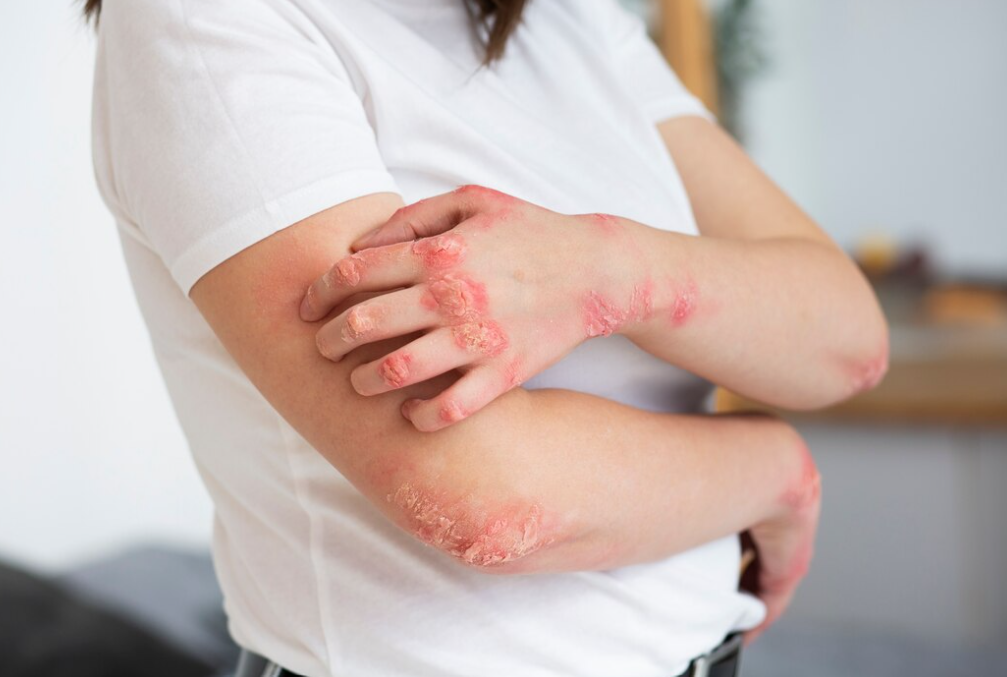
Jaundice With Itching
Pruritus is itching of the skin when you are jaundiced. The itch is caused by a build up of bile salts in the blood when the bile ducts are blocked or the liver is not working properly. This can also make the skin feel hot and uncomfortable.
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin and eyes that results from excess bilirubin deposited in the skin, and dark urine results from excess bilirubin excreted by the kidneys. The skin itches, possibly because bile products accumulate in the skin. Scratching can damage the skin.
ome people with liver disease experience skin itching all over their body or in specific areas, like the feet or arms. Itchiness is not a symptom of liver disease on its own, though.
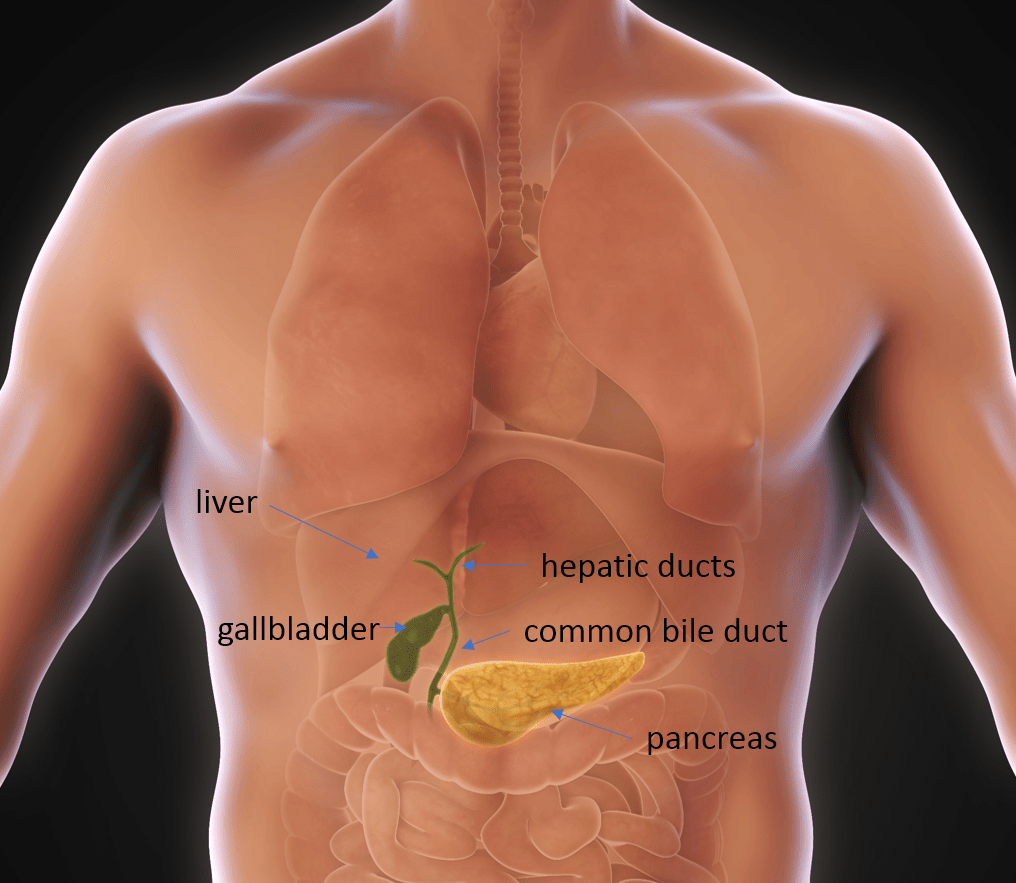
Bile duct stones
Bile duct stones are gallstones in the bile duct. They can start in the gallbladder and migrate into the bile duct or they can form in the bile duct itself. The stones can become lodged in the bile duct, causing a blockage. At the Bile Duct and Pancreatic Diseases Program, part of the University of Michigan’s Division of Gastroenterology, our multidisciplinary team provides the newest in minimally invasive treatments for bile duct stones.
These treatments are not widely available and are performed by experienced gastroenterologists with high volumes in these procedures. Gallstones and bile duct stones (also known as choledocholithiasis) are the same, just located in two different areas of the body. Stones may pass spontaneously out of the bile duct on their own. However, when a stone gets stuck in the bile duct, medical intervention is necessary, otherwise inflammation, bacterial infection, and even severe organ damage can occur.
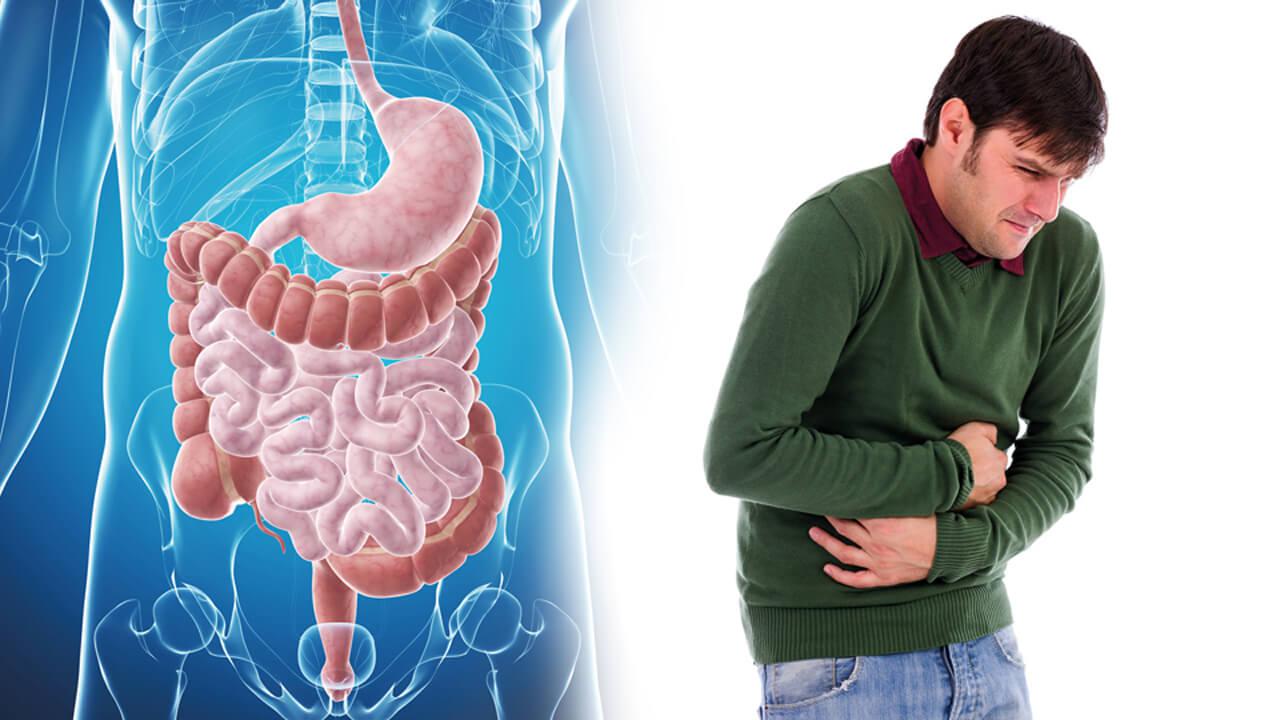
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common disorder that affects the stomach and intestines, also called the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms include cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and diarrhea or constipation, or both. IBS is a chronic condition that you’ll need to manage long term.
Only a small number of people with IBS have severe symptoms. Some people can control their symptoms by managing diet, lifestyle and stress. More-severe symptoms can be treated with medication and counseling.
IBS doesn’t cause changes in bowel tissue or increase your risk of colorectal cancer.
Why Choose Us
Complete Liver & Cancer Care Solutions For All
ExperienceTeam
+15 Yrs Experience
Standards Treatments
Best Departments
Get Appointment